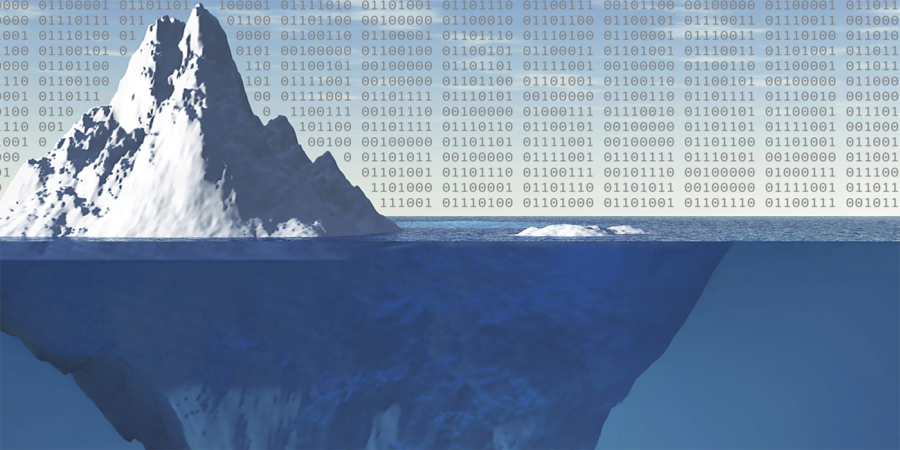
After hitting “enter,” your search engine sifts through and selects every website that remotely matches your search query, returning millions of results sorted by relevancy in fractions of a second. But what you may not realize is that all of those millions of results are just the very tip of the iceberg of the Internet — less than ten percent of the Internet is accessible through all of the traditional search engines such as Google and Yahoo combined.
Everything that can be accessed by a traditional search engine is known as the “surface web” or “clearnet,” and beyond that are the deep and dark recesses of appropriately labeled “darknets” — privately accessible networks where political activists, scammers, hackers, military bases and blatantly illegal types convene. Part of the danger of darknets lies in their accessibility — anyone with a computer and basic knowledge of the Internet can gain entrance.
It’s crazy to think that we’re completely blinded from the other 99 percent of content floating around invisibly on the deep web.
-Jerry Huang
Story continues below advertisement
“When we browse the web [through Google], we’re only getting access to one percent of the web. Think of the surface web that we use as the surface of the ocean,” junior Jerry Huang said.
A darknet is a private, restricted network that can only be accessed through specific browsers, authorizations and software configurations. They host all sorts of content that cannot be found on the surface web, and thus, are populated with troves of illegal merchandise and dangerous characters.
The popularity of darknets is on the rise, reportedly growing exponentially compared to the surface web’s. The amount of devices that can access darknets rose more than twofold between 2013 and 2014, from 1,050,000 devices to over 2,500,000, according to released data by The Tor Project, the developer of a darknet browser, Tor.
These untraceable networks arose in the 1970s when there was a need for military security due to the rising popularity of online information hosting. Military information was also stored there, and anyone with basic computer skills could find this information. This became dangerous during the Cold War when there were imminent nuclear threats from Russia, to which the U.S. Department of Defense responded by creating the Advanced Research Projects Agency Network (ARPANET) in order to preserve security for confidential military and government actions. This network essentially created “layers” to the online content, a major contribution to allowing people to browse the Internet anonymously decades later.
To access a darknet, one needs to download an application such as The Onion Router (Tor), which is the most popular method, or a similar system such as The Freenet Project or Invisible Internet Project (I2P). Upon downloading one of these applications, users are free to browse the homepage, dubbed the “Welcome Mat of the Darknet.” This front page seems like a typical clearnet page, containing links to many harmless and legal websites, but, in reality, anything is a manual search and click away.
Darknet pages are similar to surface web pages, but instead of links ending in “.com,” “.net” or “.org,” they end in “.onion. ” In an onion network, messages are encapsulated in layers of encryption, like those of an onion. They are transmitted through a series of network nodes called onion routers, due to the fact that each node “peels” away a single layer, uncovering the data’s next destination. Essentially, each node only knows the next node, so it is nearly impossible to discover the content of the original search query.
Anyone analyzing the Internet activity of a darknet user will know that network communication was taking place, but not the content of these messages nor the persons reached.
Through manual searching, one can find many links to all sorts of darknets, many of which are very much illegal. Since Tor’s main advantage is that it is private and completely anonymizes browsing, darknets are entirely anonymous and thus popular among criminals and other unsavory types. This results in there being plentiful links leading to black markets, self-harm forums, communities of anarchists, radicals, racists and just about any other group fathomable. There is truly something for everyone on the darknets.
“Most of the darknet contains content related to the online black market. You will find drugs, weapons, computer hacking, forged documents and illegal software.” Huang said. “You can buy any kind of illegal item if you wanted to.”
The marketplaces are the most frequented darknets, and therefore perhaps the most dangerous of all darknets. The high level of traffic on these pages indicates that most people visit darknets to purchase items , usually illegal substances and objects, from these marketplaces.
The Silk Road, a popular, illegal darknet drug marketplace, was shut down in late 2013 by the Federal Bureau of Investigation. Many sites like it have also been shut down by government intervention in the past, causing transactions to be halted and currency to be lost.
Darknet transactions are done with Bitcoin, an untraceable peer-to-peer cryptocurrency, as their currency of choice. Bitcoins allow for transactions on the darknet to be reliable and convenient, thus adding to the appeal of anonymous online transactions.
The marketplaces themselves are not very reliable as they are constantly being shut down as the Silk Road was, and additionally as there is always runs the risk of simply not receiving what one paid for, since the anonymous purchasing system which does not bind the seller to deliver the item. In terms of the item reviews, the sellers of such transactions will be very reliable, while the unlawfulness of the transaction itself renders it unreliable for different reasons.
Darknets are teeming with scammers and hackers, as many try to gain harmful access to a user’s computer — more specifically their bank accounts and legal identity. Potential risks of using darknets include stolen identity, robbery or computer virus transmission, which is a huge drawback to the anonymity of darknets. This gives people with computer knowledge a huge edge in the criminal world by making them incredibly dangerous on darknets, which may lead to the creation of a new kind of criminal.
All in all, they are an aspect of the modernizing world that are rising in popularity quickly, and a reminder of the transition to the digital world.
Above any of the other risks associated with using the darknet, purchasing drugs, firearms, or any other illicit merchandise over darknets is explicitly illegal. While it is no less illegal than purchasing drugs off the street, it is not caught as often as street trafficking, due to the fact that it is hard to arrest someone who is completely anonymous. This contributes to its rising popularity, as it is easier to do illegal things without getting caught, and people are always looking for the easiest way out.
However, certainly not everyone that uses darknets has to be morally corrupt or in search of partaking in unlawful activities.
“Even though darknets have negative connotations, they have benefits if used with good intentions. [They] can be used for personal privacy and the protection of individual privacy rights,” Huang said.
There are many websites within darknets that are perfectly legal in every sense of the word, much like ones on the surface web. Some users prefer darknets simply because of the privacy they ensure. Anonymous chats can take place on the darknets and people can express their opinion freely about sensitive topics such as governments and racism. Darknets can offer a community for people that have certain unique interests and passions. All in all, they are an aspect of the modernizing world that are rising in popularity quickly, and a reminder of the transition to the digital world.
Regardless, darknets are incredibly dangerous to anyone accessing them. Once on the darknet, users have access to all sorts of illicit content that is potentially very harmful to viewers. A hitman-for-hire can be bought for upwards of 250,000 dollars — that in itself speaks volumes about the content on the darknets.
“It’s crazy to think that we’re completely blinded from the other 99 percent of content floating around invisibly on the deep web. If you ever want to access it, be sure you’ve educated yourself on the risks involved,” Huang said.
Certainly the darknets garner much curiosity — in less than 10 clicks one can access the entire world of the darknets, but if you choose to use them it is imperative to tread lightly. Do not just click links without thinking about where you might end up, what you might see or who you might meet.